Throttling 이란?
- 짧은 시간 간격으로 연속해서 발생한 이벤트들을 일정시간 단위(delay)로 그룹화하여 처음 또는 마지막 이벤트 핸들러만 호출되도록 하는 것
- 주로 사용되는 예: 무한스크롤
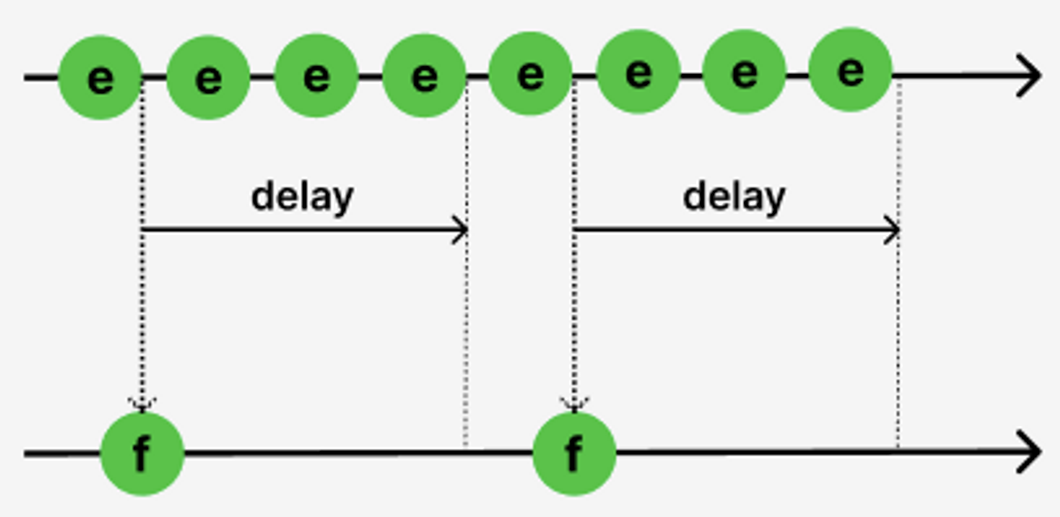
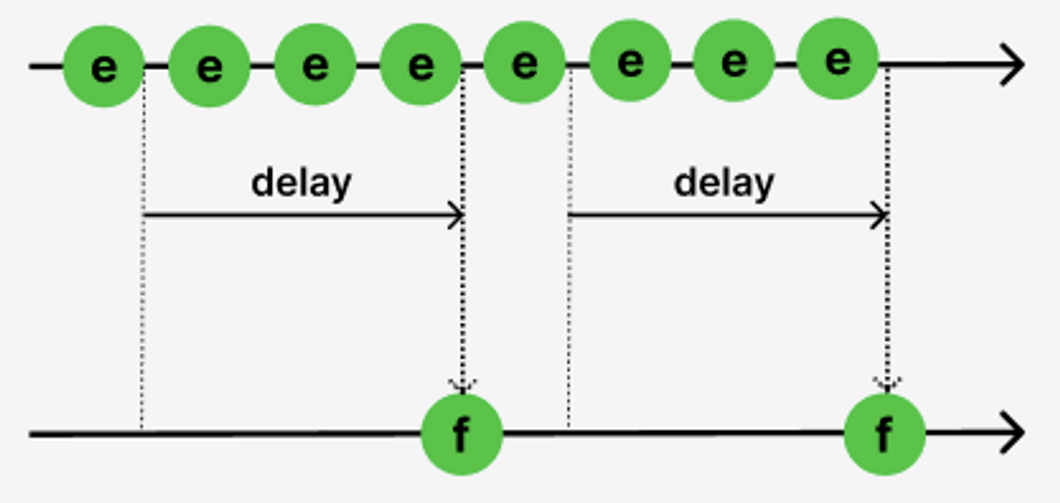
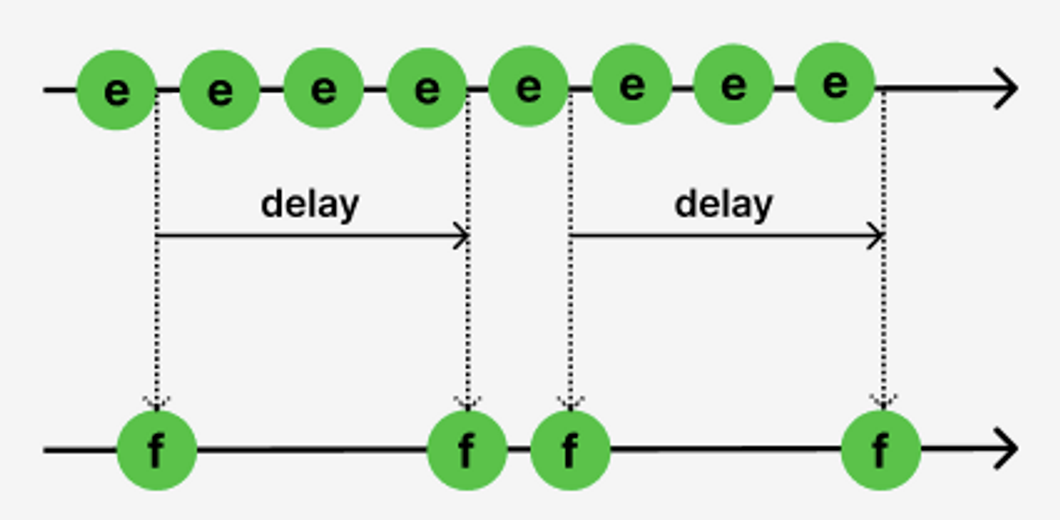
Throttling 코드 예시
// Leading Edge Throttling
const throttle: ControllDelay = (delay) => {
// timerId가 있으면 바로 함수 종료
if (timerId) {
return;
}
console.log(`API요청 실행! ${delay}ms 동안 추가 요청 안 받음`);
// n초 후에 timerId에 null을 할당함
timerId = setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`${delay}ms 지남 추가요청 받음`);
timerId = null;
}, delay);
};
Debouncing 이란?
- 짧은 시간 간격으로 연속해서 이벤트가 발생하면 이벤트 핸들러를 호출하지 않다가 마지막 이벤트로부터 일정 시간(delay)이 경과한 후에 한 번만 호출하도록 하는 것
- 주로 사용되는 예: 입력값 실시간 검색, 화면 resize 이벤트
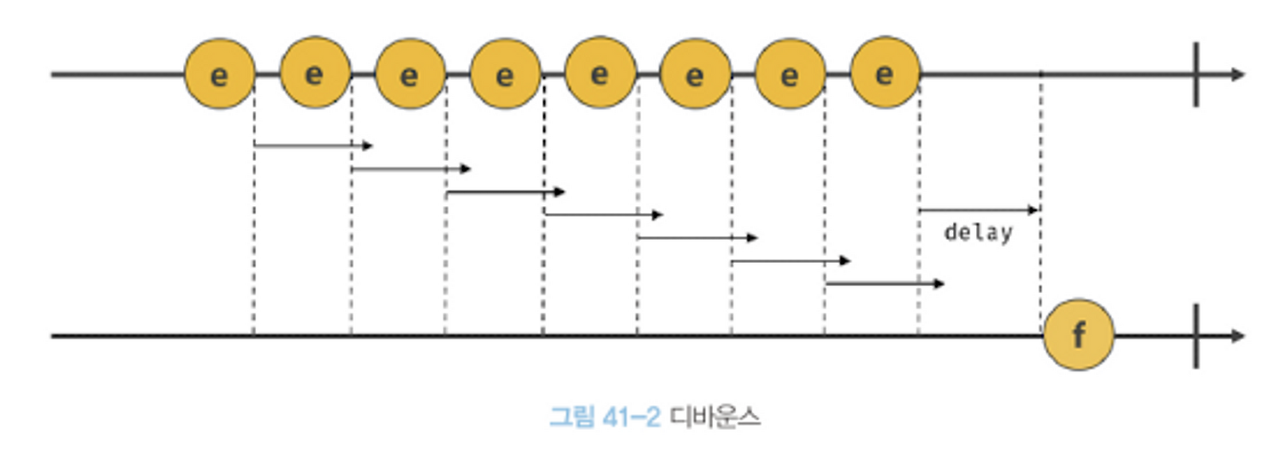
Debouncing 코드 예시
// Trailing Edge Debouncing
const debounce: ControllDelay = (delay) => {
// 할당되어 있는 timerId에 해당하는 타이머 제거
if (timerId) {
clearTimeout(timerId);
}
// timerId에 새로운 타이머 할당
timerId = setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`마지막 요청으로부터 ${delay}ms지났으므로 API요청 실행!`);
timerId = null;
}, delay);
};
메모리 누수(Memory Leak)란?
- 필요하지 않은 메모리를 계속 점유하고 있는 현상
- setTimeout 이 메모리 누수(Memory Leak)를 유발하는지?
- 하나의 페이지에서 페이지 이동 없이 setTimeout을 동작시키고 타이머 함수가 종료될 때까지 기다린다면 메모리 누수는 없다. 그런데 페이지 이동 전에 setTimeout으로 인해 타이머가 동작 중인 상태에서 clearTimeout을 안 해주고 페이지 이동 시 컴포넌트는 언마운트 되었음에도 불구하고 타이머는 여전히 메모리를 차지하고 동작하고 있다. 이 경우 메모리 누수(Memory Leak)에 해당한다고 말할 수 있다.
- 리액트로 만든 SPA 웹사이트는 페이지 이동 시 컴포넌트가 언마운트 된다.
- 결론적으로 상황에 따라 메모리 누수를 일으킬 수도 있고 아닐 수도 있는 것이다.
useEffect(() => {
// componentWillUnmount (컴포넌트가 사라지기 직전에 실행)
return () => {
// 페이지 이동 시 실행
if (timerId) {
// 메모리 누수 방지
clearTimeout(timerId)
}
};
}, [timerId])setTimeout 시 메모리 누수 방지하기
Throttling and Debouncing 실전 코드
const throttle: ControlDelay = (callback, delay) => {
let timerId: NodeJS.Timeout | null = null;
let latestArgs: any[] = [];
return (...args: any[]) => {
// For trailing edge
latestArgs = args;
if (timerId) return;
// For Leading edge
callback(...args);
timerId = setTimeout(() => {
if (!_.isEqual(latestArgs, args)) callback(...latestArgs);
timerId = null;
}, delay);
};
};const debounce: ControlDelay = (callback, delay) => {
let timerId: NodeJS.Timeout | null = null;
return (...args: any[]) => {
if (timerId) clearTimeout(timerId);
timerId = setTimeout(() => {
callback(...args);
}, delay);
};
};const selectEventControl = (delay: number) => {
switch (selected) {
case "customThrottle":
return throttle((text) => setSearchText(text), delay);
case "customDebounce":
return debounce((text) => setSearchText(text), delay);
case "lodashThrottle":
// _.throttle 의 기본 옵션은 leading & trailing edge
return _.throttle((text) => setSearchText(text), delay, {
leading: true,
trailing: true,
});
case "lodashDebounce":
// _.debounce 의 기본 옵션은 trailing edge
return _.debounce((text) => setSearchText(text), delay, {
leading: false,
trailing: true,
});
default:
break;
}
};const handleSearchText = useCallback(selectEventControl(2000), [selected]);
const handleChange = (e: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => {
handleSearchText(e.target.value);
setInputText(e.target.value);
};
useCallback 사용하는 이유
이전에 호출했던 함수를 반복적으로 호출기 위해서! (동일한 함수를 호출해서 timerId를 기억함)


